What Does Pressure Measure Apex
How to Measure Pressure?
What are the unlike types of force per unit area measurement sensors and how practice they work?
Definition, working principle and types. Become to know the functionalities and capabilities of various pressure measurement sensors in this comprehensive guide.
Force per unit area Transducers manufactured in the U.S. by FUTEK Advanced Sensor Technology (FUTEK), a leading sensor manufacturer, utilizing one of the almost advanced technologies in the Sensor Industry: Metal foil strain gauge engineering. A pressure transducer is divers as a transducer that converts an input mechanical pressure into an electrical output signal (pressure sensor definition). There are several types of pressure level transducers based on size, capacity, measurement method, sensing engineering and output requirements.
What is a Pressure level Measurement Sensor?
What does a pressure level transducer do? A pressure sensor is a transducer or instrument that converts an input mechanical pressure level in gases or liquids into an electrical output signal. A pressure transducer consists of a pressure level-sensitive element that can measure, discover or monitor the pressure level being practical and electronic components to convert the information into an electrical output indicate.
Pressure is defined every bit the amount of forcefulness (exerted by a liquid or gas) applied to a unit of "area" (P=F/A), and the common units of pressure are Pascal (Pa), Bar (bar), Due north/mm2 or psi (pounds per foursquare inch). Pressure transducers often apply piezoresistive technology, as the piezoresistive element changes its electrical resistance proportional to the strain (pressure) experienced.
How does a Pressure Measurement Sensor work?
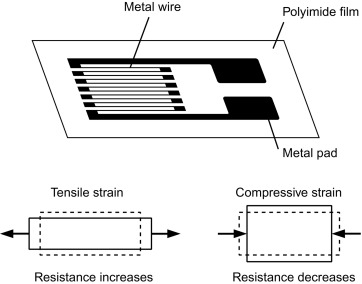
To sympathise how a FUTEK industrial pressure sensor works, firstly, one needs to grasp the underlying physics and materials science backside the pressure sensor working principle and piezoresistive consequence, which is measured by the strain gauge (sometimes referred to every bit a strain gage). A metal foil strain cuff is a transducer whose electrical resistance varies with applied pressure. In other words, it converts force, pressure, tension, compression, torque, and weight (aka weight sensors) into a change in electrical resistance, which tin then be measured.
Strain gauges are electrical conductors tightly attached to a moving picture in a zigzag shape. When this movie is pulled, it — and the conductors — stretches and elongates. When information technology is pushed, it is contracted and gets shorter. This change in shape causes the resistance in the electrical conductors to likewise alter. The strain applied in the pressure transducer tin can be determined based on this principle, equally strain estimate resistance increases with practical strain and diminishes with contraction.
Bank check out our Force per unit area Sensor Store. More than 60+ types of sensors bachelor!
Structurally, a strain gauge pressure transducer sensor is made of a metal body (besides called flexure) to which the metallic foil strain gauges are bonded. These force per unit area measuring sensors body is usually made of aluminum or stainless steel, which gives the sensor two important characteristics: (i) provides the sturdiness to withstand high pressures and (2) has the elasticity to minimally deform and return to its original shape when the pressure is removed.
A pressure sensor converts pressure into an electric signal. FUTEK industrial pressure sensors use the piezoresistive effect, which comprises of metal foil strain gauges mounted onto a diaphragm. As pressure changes, the diaphragm changes shape, causing the resistance in the strain gauges to change, allowing the force per unit area changes to be measured electrically. Our pressure sensors naturally produce an electrical signal in millivolts that varies proportionally with the pressure and the sensor excitation voltage (mV/V – millivolt per volt). Still, we offer pressure sensors with internal analog amplifiers. The pressure sensors with built-in amplifiers generate signals either in varying voltage, i.e. ±10V, or varying current (i.due east. pressure transducer 4-20ma output). However, if your application requires a digital or USB pressure sensor amplifier, please refer to our pressure sensors instruments and Amplifiers store page.
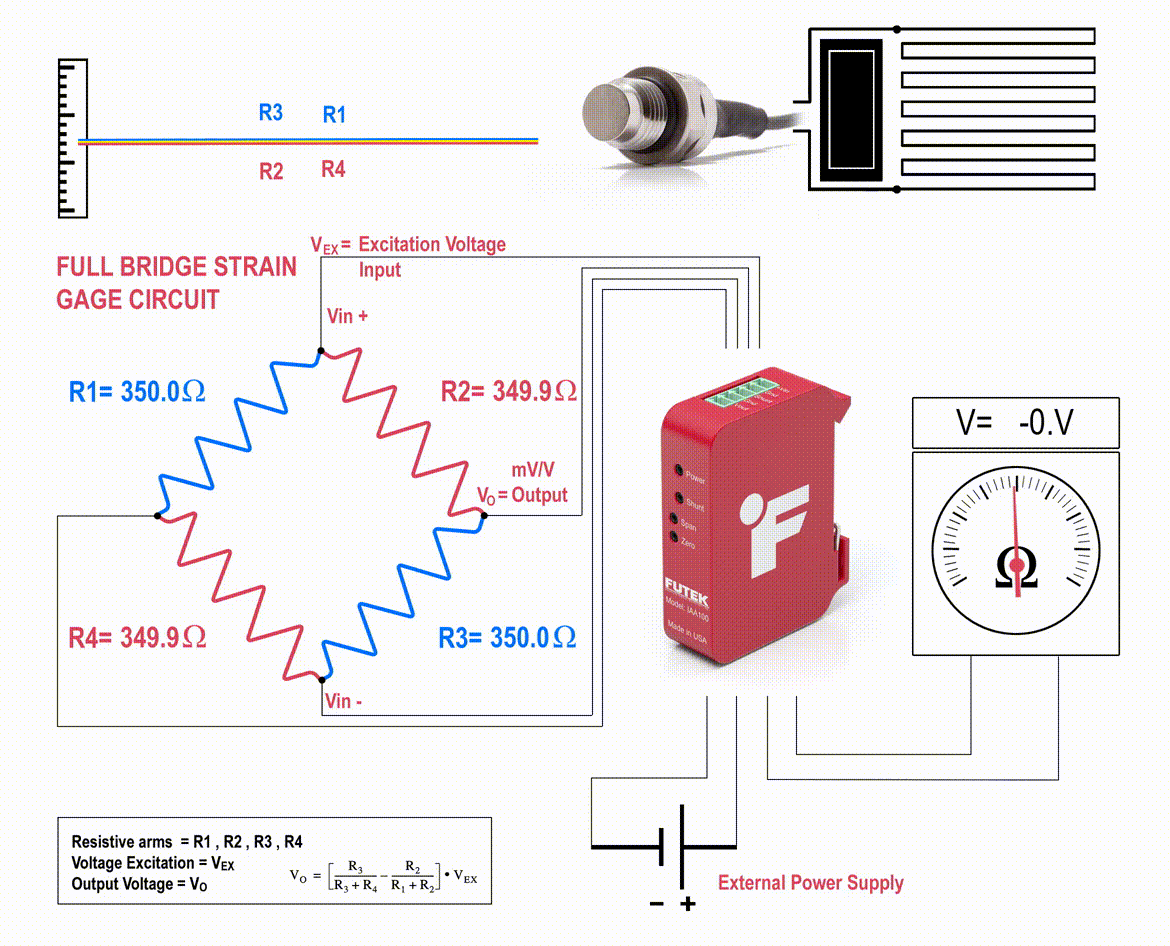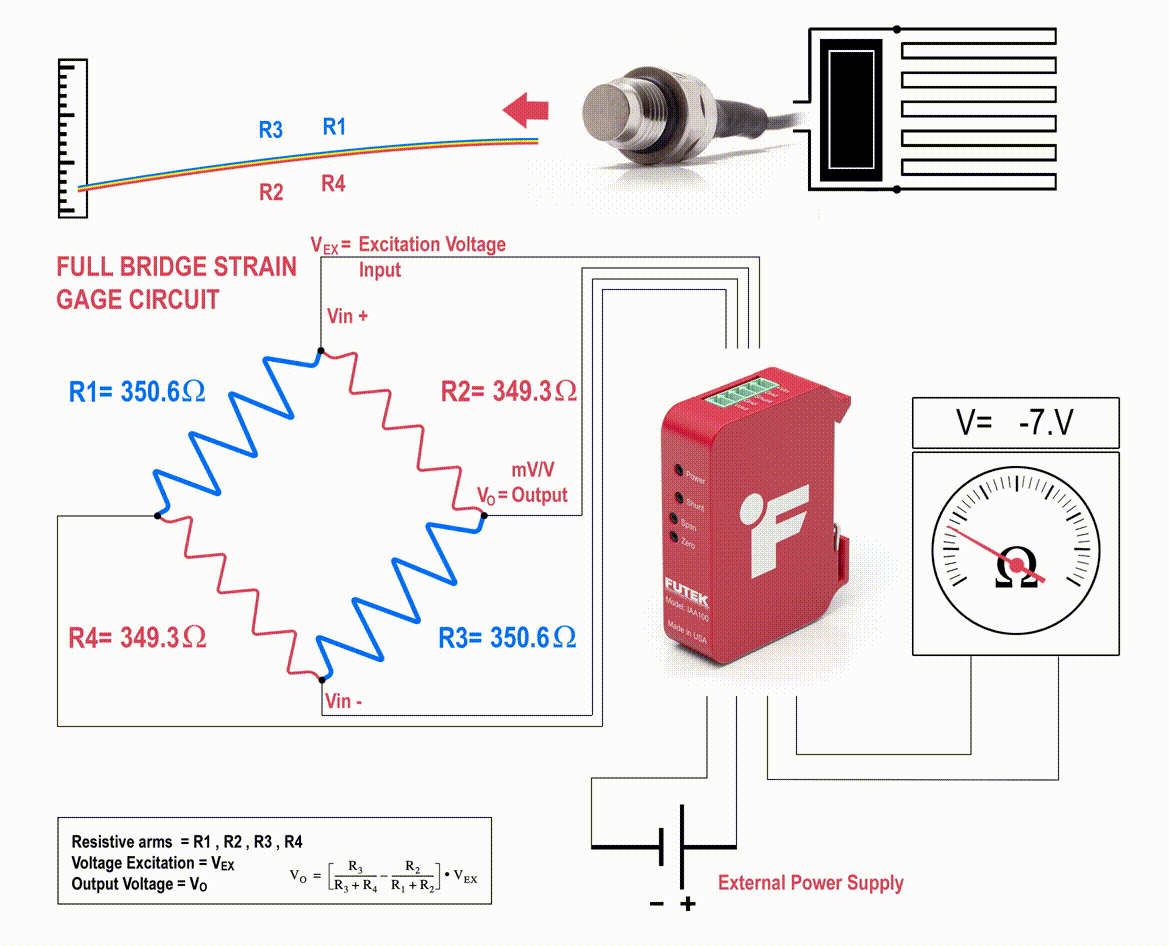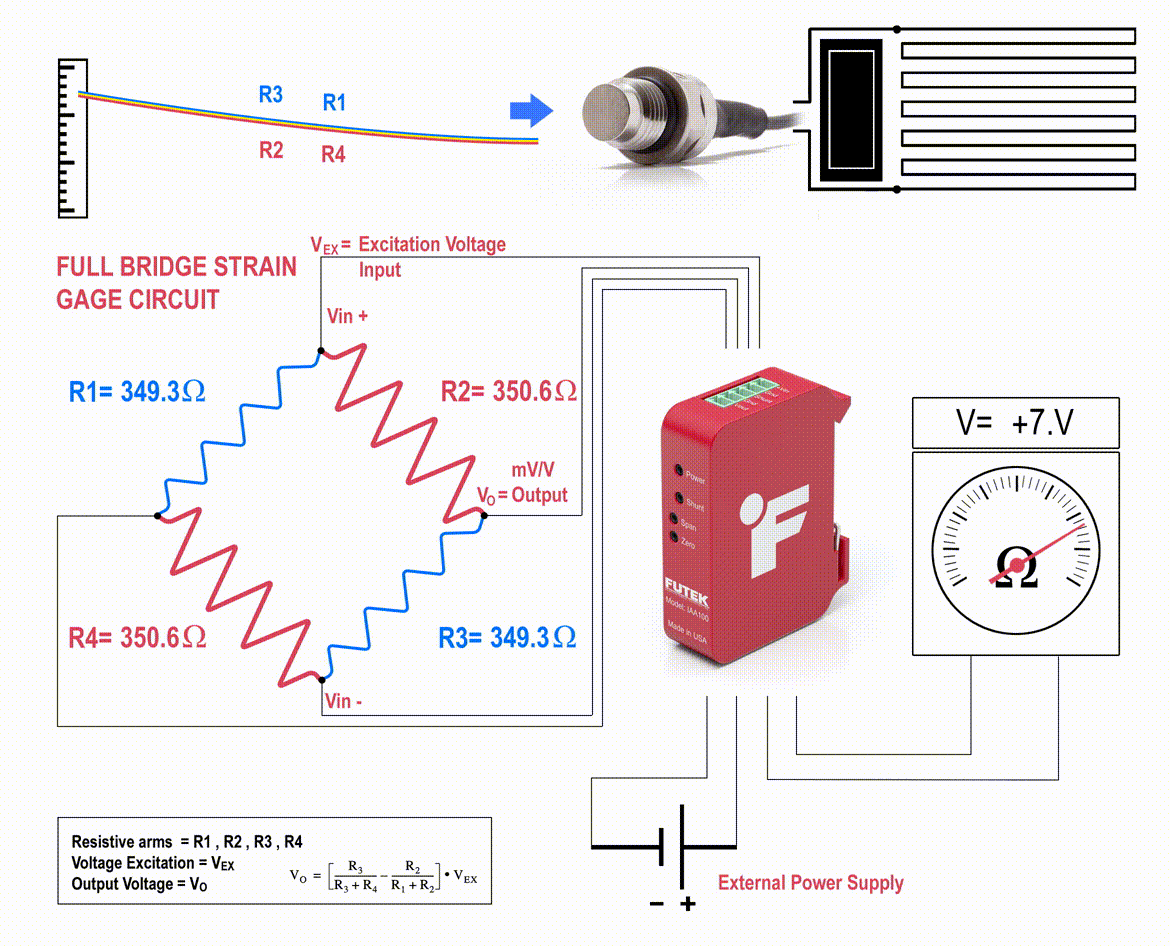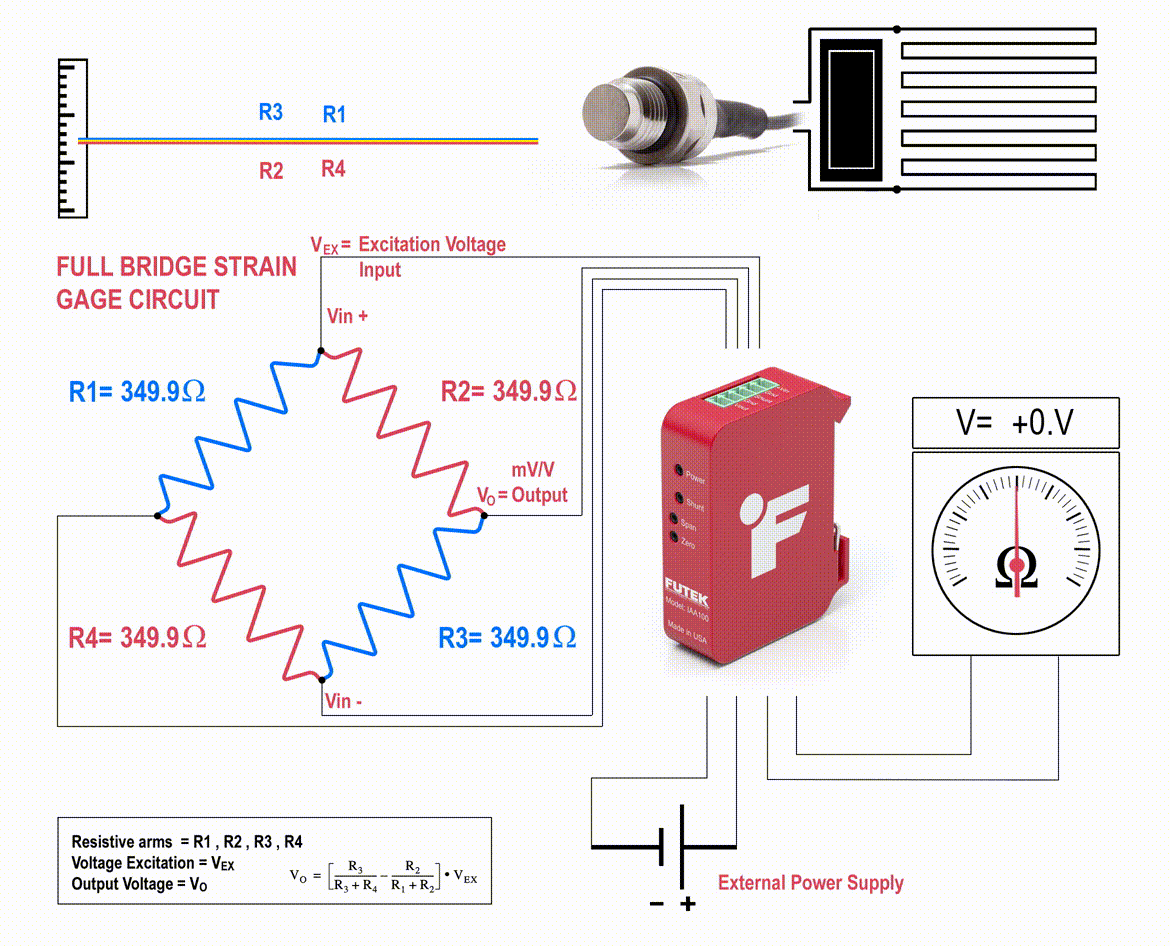
The strain gauges are arranged in what is called a Wheatstone Bridge Amplifier Circuit (come across below animated diagram). This means that four strain gages are interconnected equally a loop excursion and the measuring grid of the pressure beingness measured is aligned appropriately.
The strain gauge bridge amplifiers provide regulated excitation voltage and convert the mv/5 output betoken into another class of signal that is more useful to the user. The signal generated by the strain gage bridge is a low strength betoken and may not work with other components of the system, such as PLC, data acquisition modules (DAQ) or computers. Thus, pressure sensor signal conditioner functions include excitation voltage, dissonance filtering or attenuation, signal amplification, and output signal conversion.
Furthermore, the change in the force per unit area sensor amplifier output is calibrated to be proportional to the force per unit area applied to the flexure, which can be calculated via the pressure level sensor circuit equation.
Check out our Pressure Transducer Store. Talk to an Engineer today!
How to measure Pressure? What are the types of pressure level transducers and measurement methods?
Force per unit area sensors can be classified in terms of the type of force per unit area measurements they judge as well as the pressuring-sensing engineering science the transducer operates. In that regard, there are 3 methods to measure pressure: differential, absolute, and guess.
Differential Pressure Transducer: Differential pressure level is a measurement of the pressure difference between two pressure values or 2 force per unit area points in the system, thus measuring by how much the 2 points differ from each other, non their magnitude relative to atmospheric pressure or to another reference pressure level such equally accented vacuum. This is different from a static or absolute force per unit area sensor that would measure pressure using merely i port and typically differential pressure level sensors are packaged with 2 ports to which pipes tin exist fastened and continued to the system in ii distinct pressure points from where the differential pressure can be measured and calculated.
This pressure measuring arroyo is typically used to measure the flow of a liquid or a gas in pipes or ducts.
Accented or Vacuum Pressure Transducer: This sensor measures the accented pressure level, which is defined equally the pressure level measured relative to a perfect sealed vacuum. Accented pressure sensors are used in applications where a abiding reference is required. These applications require reference to a stock-still pressure level as they cannot be but referenced to the surrounding ambient pressure. For example, high-operation industrial applications such equally monitoring vacuum pumps, liquid pressure measurement, industrial packaging, industrial process command and aerospace and aviation inspection utilize this technique. When it comes to measuring air force per unit area, specifically for applications such equally barometric measurements for weather or in altimeters, an absolute pressure sensor is the device of choice.
Check out our Force per unit area Transducer Store. Talk to our Application Specialist today!
Guess or Relative Pressure Transducer : Gauge force per unit area is simply a special case of differential force per unit area with pressures measured differentially but ever relative to the local ambient pressure. In the same respect, absolute pressure tin can also exist considered a differential force per unit area where the measured force per unit area is compared to a perfect vacuum. Changes of the atmospheric force per unit area due to weather weather or altitude directly influence the output of a cuff pressure level sensor. A gauge pressure higher than ambient force per unit area is referred to as positive pressure. If the measured pressure is below atmospheric force per unit area information technology is chosen negative or vacuum gage pressure.
Types of pressure-sensing technologies or working principles
There are a diverseness of pressure level-sensing technologies or sensing principles capable of transducing force per unit area into a measurable and standardized electrical indicate. This article will focus on the force collector types, which are the ones that use a force guess (i.e. diaphragm) to measure strain (or deflection) due to applied force over an surface area (pressure).
Resistive or piezoresistive effect: Resistive pressure measurement sensors use the change in electrical resistance of a strain gauge bonded to the diaphragm (too known as a flexure element) that is exposed to the pressure medium.
The strain gauges oftentimes incorporate of a metal resistive element on a flexible backing bonded to the diaphragm (i.east. metal foil strain cuff), or deposited directly using thin-motion-picture show processes.
Normally, the strain gauges are continued to form a Wheatstone span circuit to maximize the output of the sensor and to reduce sensitivity to errors. This is the most usually employed sensing applied science for general-purpose force per unit area measurement and uses the same principle of how a load cell works.
Bank check out our Pressure Transducer Shop. More 60+ sensors available!
Capacitive: Capacitive pressure sensors use a diaphragm that is deflected by the applied force per unit area to create a variable capacitor to detect strain due to applied pressure. Every bit pressure is applied, the external pressure compresses the diaphragm, and the capacitance value decreases. As the pressure is released, the diaphragm returns to its original shape and capacitance follows. Common technologies use metal, ceramic, and silicon diaphragms. The capacitance can be calibrated to provide authentic pressure reading.
Capacitive sensors, which display a capacitance change as one plate deflects nether applied pressure, can be highly sensitive and withstand big overloads. Constraints on materials, and joining and sealing requirements, however, can restrict applications.
Piezoelectric consequence: Piezoelectric pressure sensors use the belongings of piezoelectric materials like ceramic or metalized quartz, to generate an electrical potential on the surface when the material is subjected to mechanical stress and strain is generated. The charge magnitude is proportional to the pressure applied, and the polarity is defined by the pressure direction. The electrical potential accumulates and dissipates apace equally pressure changes, allowing measurement of fast-changing dynamic pressures.
Force per unit area measurement standards
Pressure level is typically measured in units of strength per unit of measurement of surface surface area ( P = F / A). In physical science the symbol for pressure is p and the SI unit for measuring pressure level is pascal (symbol: Pa). One pascal is the forcefulness of one Newton per foursquare meter acting perpendicular on a surface. Other commonly used pressure units for stating the pressure level level are psi (pounds per foursquare inch), and bar. Use of pressure units have regional and application preference: psi is ordinarily used in the U.s., while bar the preferred unit of measurement of measure in Europe.
| Pascal | Bar | Standard atmosphere | Pound per square inch | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Pa) | (bar) | (atm) | (psi or lbf/in2) | |
| 1 Pa | i | x−5 bar | 9.8692×10−vi atm | 1.45 x x−4 |
| ane bar | 100,000 | 1 | 0.98692 | fourteen.5038 |
| one atm | 1013.25 | one.01325 | i | 14.6959 |
| i psi or lbf/intwo | 6,894.76 | 0.06894 | 0.06804 | 1 |
Why is it important to calibrate pressure transducer?
Force per unit area transducer calibration is an aligning or set of corrections that are performed on a sensor, or musical instrument (amplifier), to make certain that the sensor operates as accurately, or mistake-free, as possible.
Every sensor is prone to measurement errors. These structural uncertainties are the simply algebraic departure between the value that is indicated by the sensor output versus the bodily value of the measured variable, or known reference pressures. Measurement errors tin be caused by many factors:
Zero offset (or pressure level sensor goose egg balance): An kickoff means that the sensor output at zero pressure (truthful nil) is college or lower than the platonic output. Additionally, nil stability relates to the degree to which the transducer maintains its zero rest with all environmental conditions and other variables remaining abiding.
Linearity (or non-linearity): Few sensors accept a completely linear characteristic curve, significant that the output sensitivity (slope) changes at a dissimilar rate throughout the measurement range. Some are linear enough over the desired range and does not deviate from the straight line (theoretical), but some sensors crave more complex calculations to linearize the output. So, pressure sensor not-linearity is the maximum deviation of the actual scale bend from an ideal straight line drawn between the no-force per unit area and rated pressure level outputs, expressed every bit a percentage of the rated output.
Hysteresis: The maximum deviation between transducer output readings for the same applied pressure level; ane reading is obtained by increasing the pressure from goose egg and the other by decreasing the pressure from the rated output. It commonly measured at half rated output and expressed equally a pct of the rated output. Measurements should be taken every bit rapidly as possible to minimize creep.
Repeatability (or non-repeatability): The maximum difference between transducer output readings for repeated inputs under identical pressure and environmental conditions. It translates into the sensor'south ability to maintain consistent output when identical pressure level are repeatedly applied.
Temperature Shift Bridge and Zero: The change in output and zero rest, respectively, due to a change in transducer temperature.
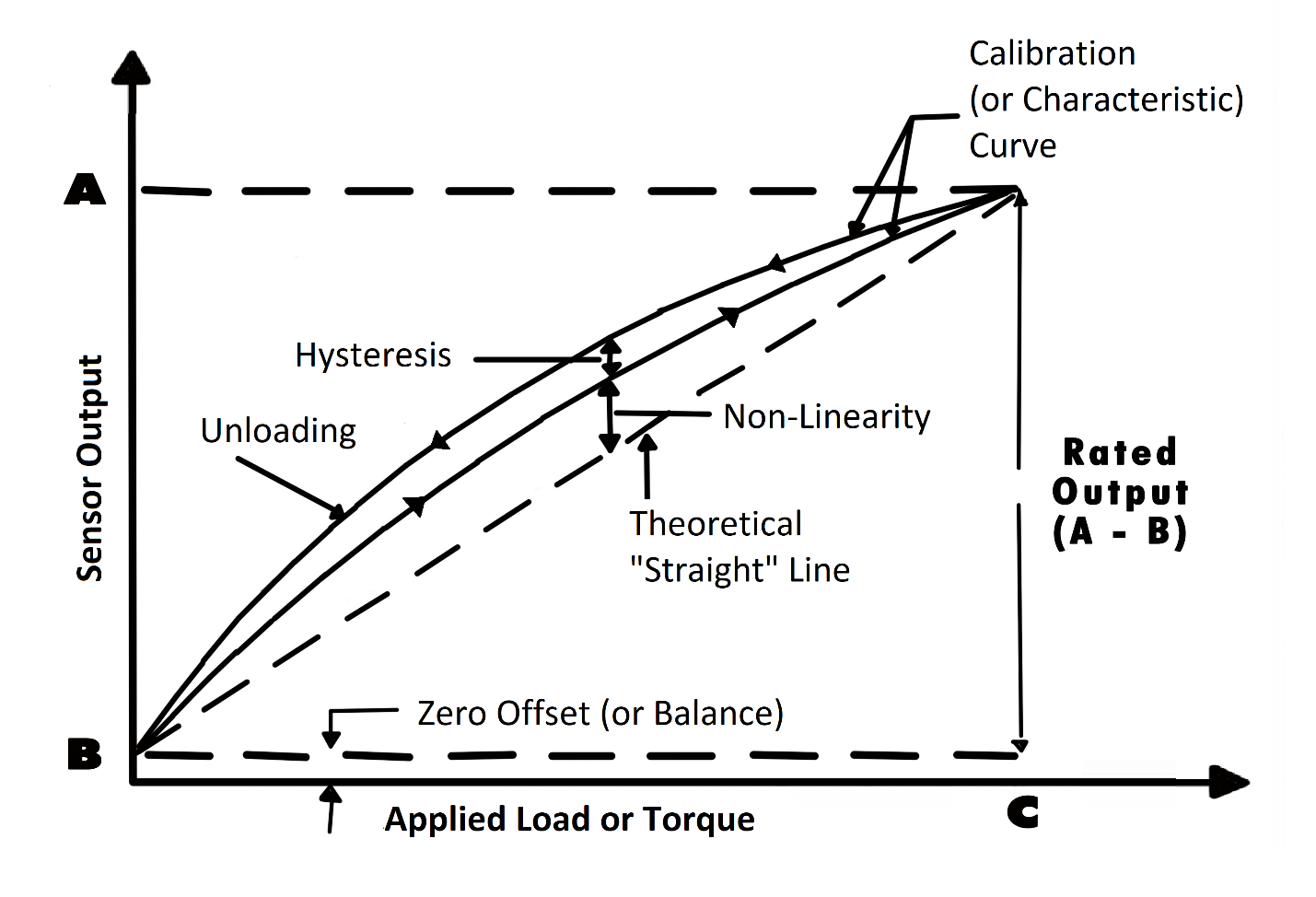
Each force per unit area sensor has a "characteristic curve" or a "scale curve", which defines the sensor's response to an input. During a regular calibration using the sensor calibration machine, nosotros cheque the sensor'due south nada offset and linearity past comparing the sensor output under reference weights and adjusting the sensor response to an ideal linear output. The pressure sensor calibration equipment also check hysteresis, repeatability and temperature shift when customers request it for some disquisitional pressure level measurement applications.
For more data about calibration, delight refer to our Sensor Calibration FAQ Page.
If you have further questions most calibration terms and definitions, please refer to our Sensor Scale Terms Glossary.
Desire to know what calibration services we offer for your sensor and/or arrangement?
Contact us to learn more!
How often should a pressure level transducer be recalibrated?
As strain gauge pressure transducer sensor are exposed to continuous usage, aging, output migrate, overload and improper handling, FUTEK highly recommends a yearly recalibration interval. Frequent recalibration helps confirm whether the sensor maintained its accuracy over time and provides a load cell calibration certificate to bear witness that the sensor still meets specifications.
However, when the sensor is used in critical applications and harsh environments, pressure level sensors may crave even more frequent calibrations. Please consult appropriate calibration intervals with our Technical Support team, who will help you lot evaluate the nigh economical calibration service interval for your sensor.
What Does Pressure Measure Apex,
Source: https://www.futek.com/how-to-measure-pressure
Posted by: merrittwenctim.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Does Pressure Measure Apex"
Post a Comment